Activity: MOS Transition Frequency
ctivity: MOS Transition Frequency
- Instructions: This activity is structured as a tutorial with an activity at the end. Should you have any questions, clarifications, or issues, please contact your instructor as soon as possible.
- At the end of this activity, the student should be able to:
- Plot the frequency response of NMOS and PMOS transistors.
Activity 1: NMOS Transition Frequency
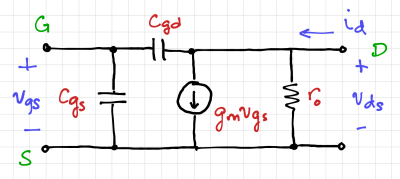
At high frequencies, the MOS gate-to-source capacitance, and the gate-to-drain capacitance, limits the MOSFET current gain at high frequencies, and thus, needs to be included in the two-port model, as shown in Fig. 1. The short-circuit current gain can be expressed as:
We then define the transition frequency, as the frequency when magnitude of the short-circuit current gain is equal to 1, or:
Thus, we get:
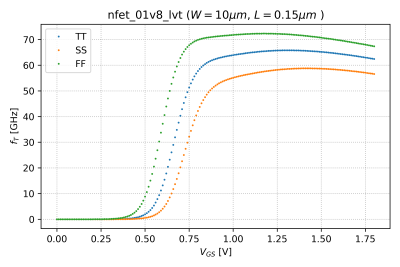
We can determine the transition frequency by running an AC analysis to get the frequency response of the NMOS transistor, . Thus, transition frequency is the frequency when the short-circuit current gain drops to 1, or equivalently 0 dB.
You can modify this sample schematic and Python script to generate the plot of the NMOS transition frequency as a function of , and shown in Fig. 2.
What happens to the transition frequency when you independently:
- Change the length to and
- Change number of fingers to
Plot the resulting . Is this what you expected? Why?
Activity 2: PMOS Transition Frequency
Repeat Activity 1 for the 1.8V LVT PMOS transistor. For the same size, how does the of the PMOS compare to the NMOS? Comment on the relative values as well as on the effect of process variations.
Report Guide
Write up a report (maximum of 5 pages including figures) answering the questions above. Include annotated graphs showing the different regions of operation for both the NMOS and PMOS transistors.
Submission
This activity is for both graduate and undergraduate students. For UP students, the submission bin link will be posted in Piazza.